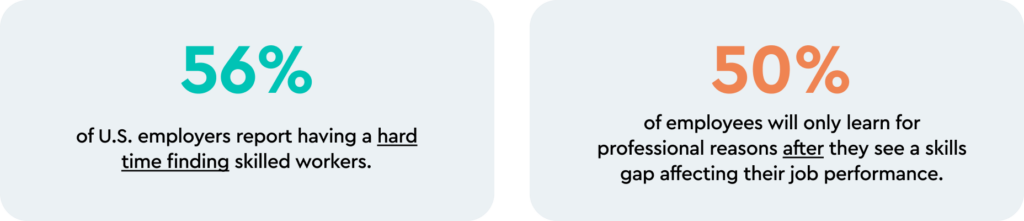
The U.S. economy loses $1.3 trillion a year due to the skills gap, and a whopping 56% of U.S. employers report having a hard time finding skilled workers. But 50% of employees will only learn for professional reasons after they see a skills gap affecting their job performance. So it’s often falling to the organizations themselves to develop upskilling programs to stay competitive and develop their own workforce.
What is Upskilling?
Before delving into the intricacies of upskilling, it’s crucial to understand the difference between upskilling and reskilling. While both terms involve learning new skills, upskilling focuses on enhancing existing skills and making employees more proficient in their current roles. This sets the foundation for a workforce that can adapt to evolving demands.
The most common areas to focus on upskilling are:
Hard skills
Often referred to as technical skills, hard skills are tangible and quantifiable abilities that are specific to a particular job or task. Examples include coding, data analysis, language proficiency, and engineering knowledge. Hard skills are highly job-specific and are essential for the performance of certain roles.
Soft skills
On the other hand, soft skills are interpersonal or people skills. These encompass attributes like communication, teamwork, leadership, and adaptability. Soft skills are generally more transferable than hard skills and can be valuable in various job roles and industries.
Leadership development
Leadership development is the intentional process of cultivating and enhancing the skills, attributes, and behaviors necessary for effective leadership roles within an organization. It involves targeted training and experiences aimed at preparing individuals to lead and inspire teams, make strategic decisions, and navigate the complexities of leadership responsibilities.
Examples of Successful Upskilling Programs and Methods
Upskilling is not a one-size-fits-all concept. It encompasses various dimensions and often a combination of all three of these upskilling areas of focus. To ensure a well-rounded upskilling strategy, companies need a holistic approach to address diverse skill sets within their workforce and cater to the specific needs of their industry.
Exploring practical examples of upskilling initiatives sheds light on the diverse ways organizations can approach this challenge. These can include:
- Technical training: Many technology-driven industries implement technical training programs to keep employees abreast of the latest tools, programming languages, and industry-specific technologies. For instance, a software development company might provide coding bootcamps or certifications to enhance the technical skills of its workforce.
- Fostering soft skills: Soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, and adaptability, are critical for success in various job roles and industries. Upskilling programs focused on soft skills might include workshops, coaching sessions, or experiential learning opportunities. For example, a customer service-oriented business might provide training to enhance employees’ communication and empathy skills when dealing with clients.
- Leadership workshops: Organizations often conduct leadership workshops aimed at developing essential leadership skills among employees. These workshops may cover topics such as effective communication, strategic decision-making, and team management. Investing in leadership development ensures that employees are equipped to take on leadership roles and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
The Benefits of Upskilling
The advantages of upskilling are far-reaching and contribute to both individual and organizational growth. Breaking down these benefits provides a comprehensive understanding of why upskilling is a strategic imperative:
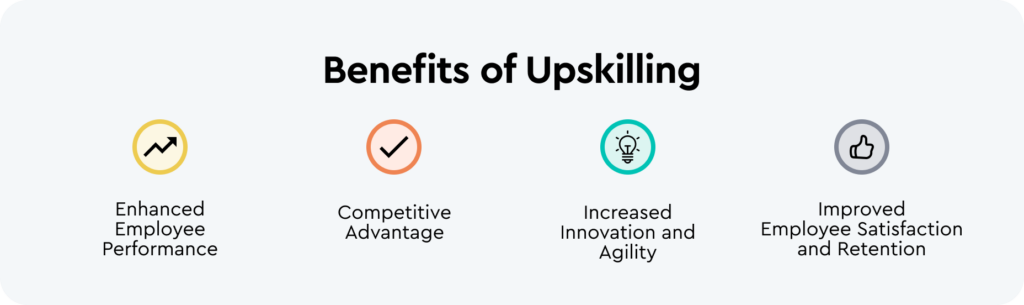
- Enhanced Employee Performance: Upskilling leads to improved productivity and efficiency. Employees equipped with advanced skills can navigate their tasks more effectively, contributing to overall performance and quality of work.
- Competitive Advantage: Staying ahead in a rapidly evolving market is a key benefit of upskilling. Companies that invest in continuous learning gain a competitive edge by ensuring their workforce remains adept at handling emerging challenges and opportunities.
- Increased Innovation and Agility: Upskilling fosters a culture of creativity and adaptability. Employees with enhanced skills are more likely to generate innovative ideas and respond flexibly to industry changes, driving overall organizational agility.
- Improved Employee Satisfaction and Retention: Demonstrating investment in employees’ growth boosts morale and loyalty. Upskilling initiatives contribute to higher job satisfaction and improved retention rates, creating a positive work environment.
How Upskilling Impacts Organizational Growth
Upskilling plays a pivotal role in organizational growth, ultimately leading to incredible benefits that bring both profitability and prosperity. The top 3 ways upskilling impacts organizational growth are:
1. Accelerated Career Development
Upskilling provides learners with the knowledge and skills needed to advance in their careers. It opens doors to new opportunities and positions within the organization, fostering a culture of continuous growth and development.
By investing in upskilling, organizations cultivate a pipeline of skilled individuals ready to take on leadership responsibilities. This proactive approach ensures a pool of qualified candidates for key roles, contributing to long-term organizational success.
2. Increased Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains
Upskilling enhances employee satisfaction and engagement, reducing turnover rates. The cost of recruiting, onboarding, and training new employees is significantly higher than retaining existing talent. Upskilling, therefore, becomes a strategic investment in retaining valuable personnel.
Instead of seeking external hires, upskilling allows organizations to tap into the potential of their current workforce. This not only saves recruitment costs but also ensures that employees are well-versed in the company’s culture and operations, leading to increased efficiency.
3. Strengthened Company Culture
Upskilling fosters a culture of continuous learning within the organization. When employees perceive that their development is a priority, it creates a positive environment where learning is embraced, contributing to a dynamic and forward-thinking company culture.
Employees who undergo upskilling programs often develop a shared language and skill set. This common ground enhances collaboration and teamwork, as employees can better understand and complement each other’s strengths, ultimately driving collective success.

4 Simple Steps to Implement an Upskilling Program
Now that you know what goes into an effective upskilling program, the challenge is to implement one. While every program is different and should be unique to your organizational and learner needs, here are four practical steps you can follow to implement an upskilling program:
1. Assess the company’s and employees’ needs
Conduct a Skills Gap Analysis: Identify the current skill sets of your workforce and compare them with the skills required for current and future roles. This analysis will help pinpoint areas where upskilling is most needed.
Seek Employee Input: Involve employees in the assessment process by gathering feedback on their own perceived skill gaps and professional development goals. This ensures that the upskilling program addresses individual needs.
2. Design tailored upskilling programs
Customize Content: Develop upskilling content that is specific to the identified needs. Whether it’s technical training modules, leadership workshops, or soft skills development, tailor the content to resonate with the roles and responsibilities within your organization.
Consider Various Learning Modalities: Recognize that individuals have different learning preferences. Incorporate a mix of online courses, workshops, mentorship programs, and hands-on experiences to cater to diverse learning styles.
3. Provide continuous support and resources
Establish Learning Communities: Foster a sense of community among learners by creating forums or groups where they can share experiences, ask questions, and support each other. This encourages a collaborative learning environment.
Offer Learning Resources: Provide access to a variety of resources, such as eBooks, articles, and industry-specific materials, to supplement the formal upskilling programs. This empowers employees to take control of their learning journey.
4. Measure and evaluate the effectiveness of upskilling initiatives
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Clearly outline the KPIs that align with the goals of the upskilling program. These could include improvements in job performance, completion rates, and employee satisfaction.
Collect Regular Feedback: Implement tools for ongoing feedback from participants. This could involve surveys, focus groups, or one-on-one discussions to understand the impact of the upskilling initiatives on individuals and the organization.
Conclusion
The journey towards a skilled and adaptable workforce requires a commitment to continuous learning, fostering a culture that embraces growth, innovation, and the pursuit of excellence. As the skills gap narrows through strategic upskilling initiatives, businesses can better position themselves and their employees for lasting success.
Adopting virtual learning tools and video + feedback solutions like GoReact can enhance your ability to develop new skills, assess competencies, and ensure lifelong learning — so you can prepare and support learners and the overall organization effectively.