Higher education institutions are under immense pressure to ensure their graduates are not only knowledgeable but also ready to enter the workforce. Employers are increasingly looking for candidates who can hit the ground running with practical, hands-on skills. This has led to a paradigm shift in education, emphasizing skills-based learning over traditional learning methodologies. The challenge for educators is to find effective ways to help students practice, reflect, and receive feedback on their skills development, ensuring they are prepared for real-world demands. In this blog you will discover skill-based education examples you can implement.
What is Skills-Based Learning?
Skills-based learning is an educational approach that focuses on the acquisition and application of practical skills that are directly relevant to real-world scenarios. Unlike traditional education models that prioritize theoretical knowledge, skills-based learning prepares students for the workforce by equipping them with the abilities they need to perform specific tasks and solve practical problems.
This approach is critical for work-readiness, as it bridges the gap between classroom or online learning and the competencies required in professional settings. Skills-based learning fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to learn and adapt continuously — skills that are indispensable in any career and are particularly valuable in today’s job market.
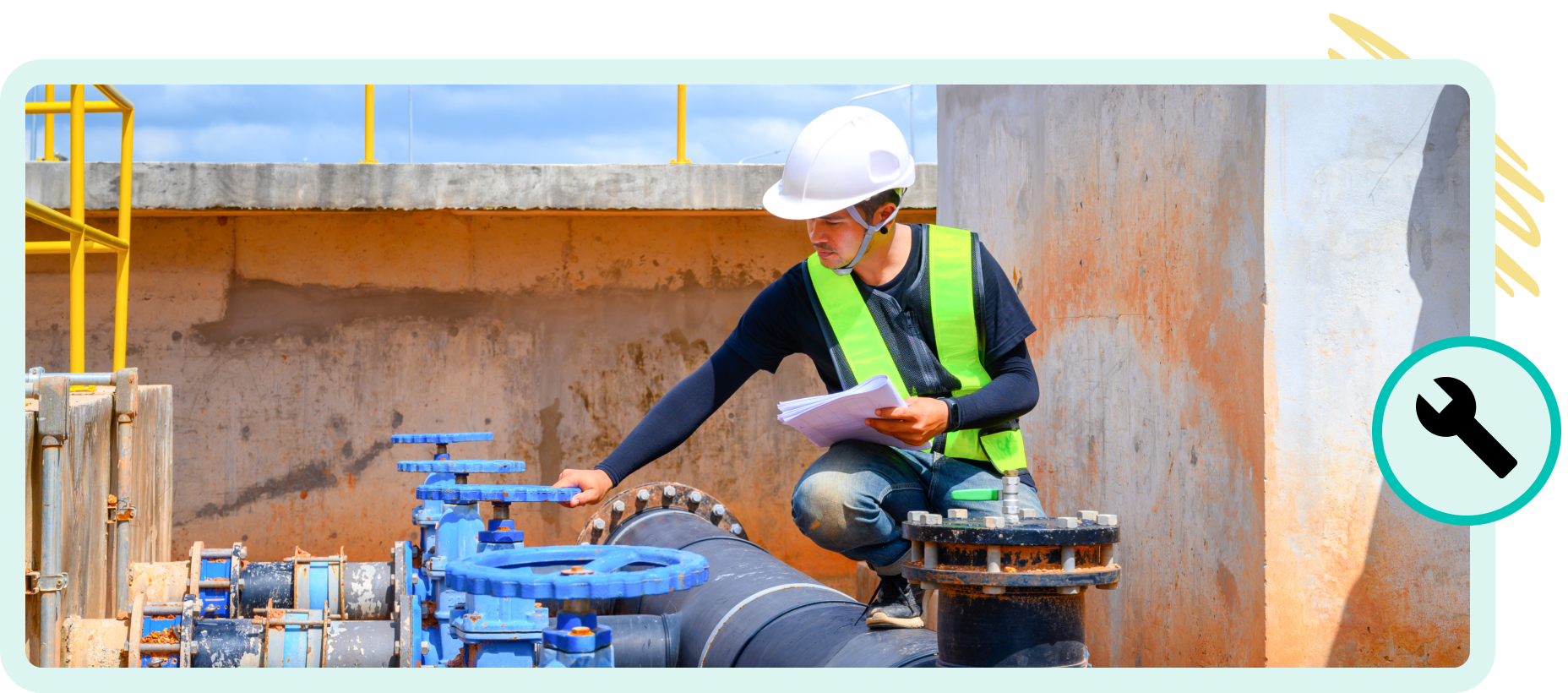

Skill-Based Education Examples for Any Discipline
Skills-based learning can be effective for any skill across any industry. Each field has unique requirements, but the core principle of practicing skills, reflecting on performance, and receiving feedback remains consistent. Here are just a few skill-based education examples that can be applied in many different areas:
- Teacher Education: In teacher education programs, student teachers learn to develop lesson plans, deliver instructions, and manage classrooms. Through skills-based learning, aspiring teachers can practice these tasks in simulated classroom environments, allowing them to refine their teaching methods and receive feedback from instructors and peers. For example, a student teacher might record a mock lesson and then review the video to identify areas for improvement.
- Communications and Business: In fields like communications and business, skills-based learning involves crafting presentations, conducting negotiations, and managing projects. Students might engage in role-playing exercises to simulate business negotiations or project management scenarios, receiving real-time feedback on their performance. This hands-on practice helps them develop the confidence and competence needed to excel in professional settings.
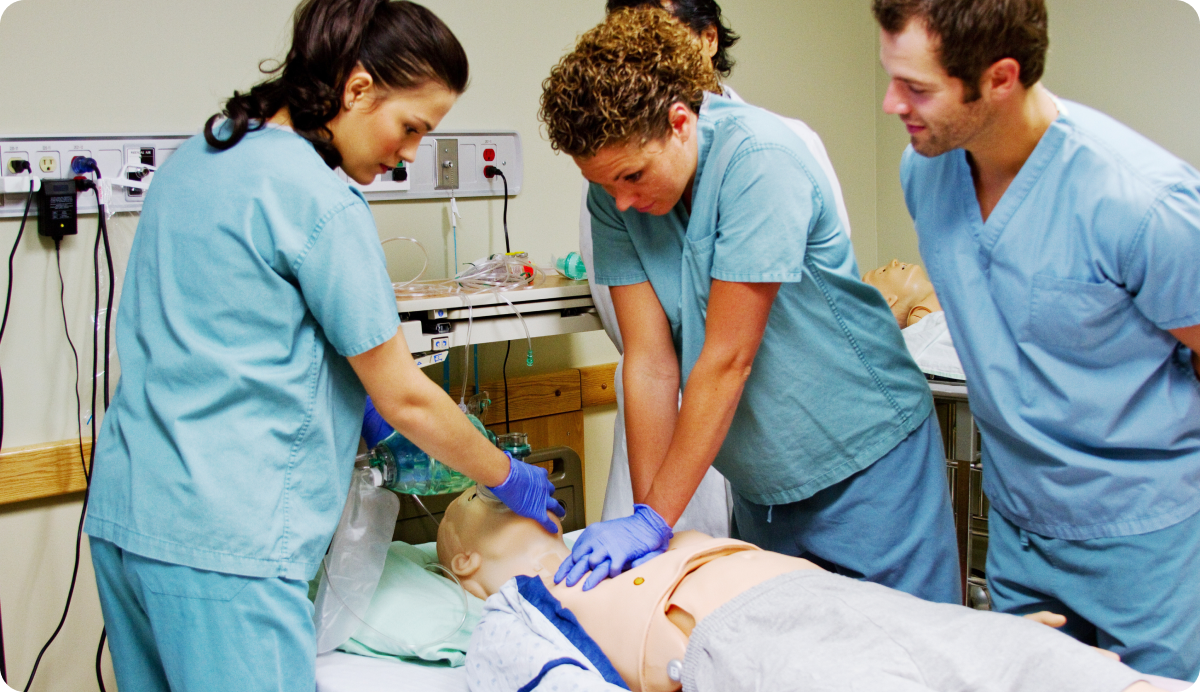
- Nursing, Counseling, and Healthcare: For nursing and counseling students, practical skills are paramount. They need to perform patient assessments, conduct therapy sessions, and manage patient care effectively. Skills-based learning in these fields often involves clinical simulations where students can practice their skills in a controlled environment. This allows them to make mistakes and learn from them without putting real patients at risk.
- Trades and Field Work: In trades such as plumbing, electrical work, or carpentry, as well as field work like environmental science or archaeology, skills-based learning is crucial for developing technical expertise. Learners might engage in hands-on workshops, apprenticeships, or field simulations where they can practice their trade skills in real-world settings. For example, an electrical apprentice might practice wiring a circuit and then receive immediate feedback on their technique and safety measures. This practical experience is essential for mastering the hands-on skills required in these fields and ensuring job readiness.
The Key to Successful Skills-Based Learning
The core of an effective skills-based learning program is incorporating the continuous cycle of practice, reflection, and feedback. This iterative process ensures that students are constantly improving and adapting their skills.
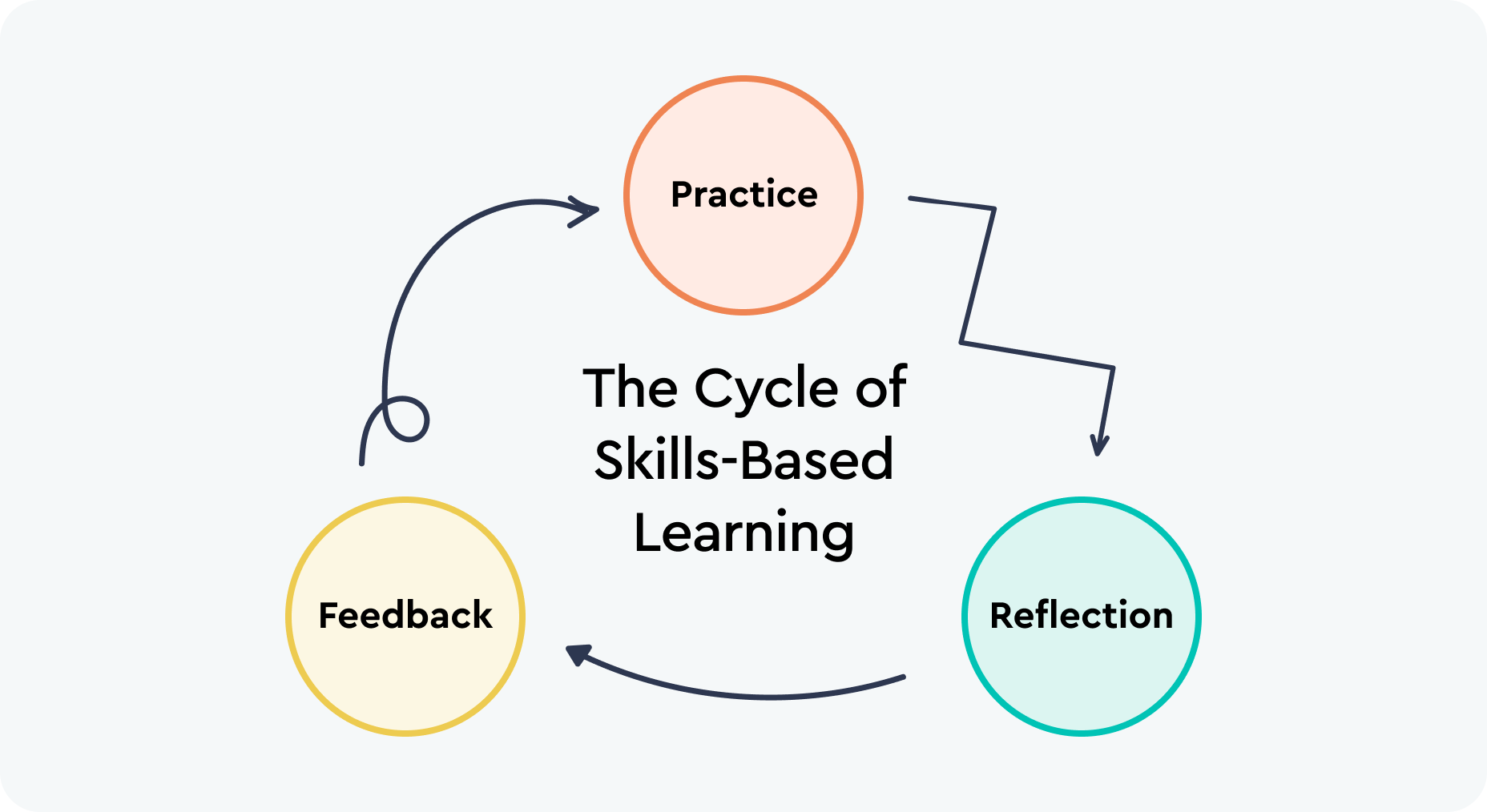
Step 1: Practice
Applying knowledge learned in the classroom to real-world applications is the first step in the cycle. For instance, nursing students might simulate patient care scenarios to hone their skills. By engaging in practical exercises, students can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application. This hands-on practice is crucial for building competence and preparing for the workforce.
Step 2: Reflect
Self-reflection is a crucial part of the learning process, helping students identify areas for improvement. Reflecting on their performance allows students to critically assess their strengths and weaknesses. For example, business students might review their presentation recordings to assess their delivery and content. This introspective process is essential for personal growth, skill development, and job-readiness.
Step 3: Feedback
Feedback from instructors and peers plays a critical role in guiding learning. The process of giving and receiving feedback helps students understand how they can improve and reinforces learning. The experience of giving feedback to peers also prepares students for the collaborative nature of the workplace. For instance, student teachers might critique each other’s lesson plans, offering constructive suggestions for improvement.
Faster Feedback Fuels Deeper Learning
Immediate feedback is most beneficial to learning. Today’s students expect rapid responses, and providing instant feedback helps maintain learning momentum. Real-time feedback allows students to quickly correct mistakes and build upon their skills.
Video is an ideal tool to leverage for skills-based learning as it allows students to practice anywhere. Video recordings provide evidence of practice and allow instructors to observe from anywhere. Video + feedback tools like GoReact make it easy to provide the best type of feedback in powerful ways:
- Instant Feedback with AI-Enabled Tools: Comments and markers can be added instantaneously, saving instructors time and giving students immediate feedback. This not only enhances the learning experience but also ensures that feedback is timely and relevant. The AI Assistant in GoReact can even help automate repetitive feedback, saving teachers time and empowering students with information faster.
- Time-Stamped: Students can see precise moments that need improvement, allowing for focused improvement and learning. Time-stamped feedback helps students understand exactly where they need to make adjustments, making the feedback more actionable.
- Personalized Feedback: Since the AI-enabled features in GoReact can automatically provide repetitive feedback, instructors can instead concentrate on providing deeper, more meaningful feedback, rather than just marking basic errors. This allows for a more nuanced and comprehensive approach to skill development and student learning.
By integrating AI and real-time feedback into skills-based learning, educators can ensure that their students are mastering the skills needed for success across various industries. GoReact enables the recording and review of student performances, providing concrete evidence of progress and areas needing improvement. Applicable to any field — from arts and sciences to trades and healthcare — GoReact supports the essential practice-reflect-feedback cycle, enhancing traditional teaching methods and streamlining the workload for educators. This dynamic, interactive learning environment helps students achieve mastery more efficiently, preparing them for their professional lives with the skills and confidence needed to succeed.
Discover how GoReact’s skill-based education examples can start accelerating education at your institution.